Is Your WordPress Website SEO Friendly?

If we could just throw in a bunch of keywords before and call it SEO, we wouldn’t have to monitor so much today. Especially with algorithms changing so often.
However, if you do want your WordPress site to thrive, you have to stay among the first five pages on the search that account for 67.60% of the clicks.
Are you not sure whether your SEO is fine? Do you want to know what is stopping you from ranking higher? Then here are the 7 tell-tale signs that your WordPress website is not SEO-friendly.
1. Slow Loading
In a nutshell, 53% of online users will abandon the site if it takes more than 3 seconds to load. We are used to instant access to the information and we know that there are many other websites that will provide information quicker. Google appreciates speedy websites as well (its aim is half a second) and ranks them higher.
In order to measure the loading speed, you can use such tools as WebPageTest or PageSpeed Insights.
If you have noticed that your WordPress website is slow, here are a few quick steps you can take.
Opt For Better Hosting

You need to choose a hosting provider and plan depending on the size of your website. A small, shared hosting might work fine for websites that have less than 1,000 daily visitors. However, if you have a massive website, would need to scale up your plan to effectively handle such traffic volumes. In addition, we always recommend choosing a reliable host with built-in caching options like WP Engine (which is what WPExplorer uses) to help improve overall site performance.
Reduce Images Size

Images are usually heavier than anything else and are usually one of the main reasons behind the slow site. Reduce the size without losing the quality on your own – through Photoshop or a free online tool like Kraken. Or you can go for plugins like the free EWWW Image Optimizer or premium WPCompress.
Minimize CSS and JS Files

Reduce the CSS and JS calls and the number of files on your site. There are manuals provided by Google you can use to do this manually, or you can use a plugin such as Autoptimize to manage this process for you. Key points to keep in mind include:
- Use CDN to adjust to internet speed in different countries
- deactivate unused plugins
- clean database (unwanted data, bot comments, old drafts, etc.)
- reduce the number of external scripts
2. Non-Responsive Design
Smartphones have probably become a bigger part of our lives than computers. We can imagine going on vacation or just for a walk in the park without the laptop. But smartphones? It has to be glued to our hands at all times. It is just faster to unlock the phone and search rather than wait for the computer to load.
So mobile traffic has consistently reached over 50% throughout 2020, meaning that you may be losing 50% of traffic just because you do not have a mobile-friendly version of your website. And no, no one is going to stay on the website to zoom in on ridiculous-looking slides and layouts, no matter how good the content is.
You can create a responsive design on your own. This might make sense if you do not want to change your current theme, however it will require coding knowledge and takes a lot of time and testing.
You can also use plugins like JetPack or WP touch to help you create a mobile version with your current theme. It is easier than doing it on your own but still not the easiest option.
But your best choice is to simply choose a responsive theme. WordPress offers numerous free themes that do have a responsive design. And pretty much all premium themes are responsive as well. The benefit here is everything has been coded and tested by the theme developer to ensure you site looks great on mobile. So you do not need to do any unnecessary work.
Take a look at the Total WordPress theme for example. This theme has been expertly coded with a fluid, responsive design to look great on any device. Plus there are even customizable break point settings if you really want to fine tune your site layouts.
For more details you could read through this WordPress guide, but really you should be fine so long as you choose a well coded, responsive WordPress theme.
3. Confusing URL Structure

Neat URLs are important for algorithms mostly, not the readers. A good URL should contain the main topic of the article and major keywords because bots read it as we, regular users, read titles. If the link consists of random numbers and letters, the bot will not even crawl deeper into the web page.
Yet, keep in mind that users are also not likely to follow a sketchy link. Therefore, you have two great reasons to level up your URL game.
Permalinks Structure
In order to change the way URLs are created, visit the admin board of the WordPress site, go to Settings, and find the section for Permalinks. Your setting now is probably date and time, it is better to go for a post name (note – if you’ve already created content with a different URL structure, you might want to also checkout our guide to changing permalinks just to be sure you don’t hurt your SEO on accident).
URL Slugs
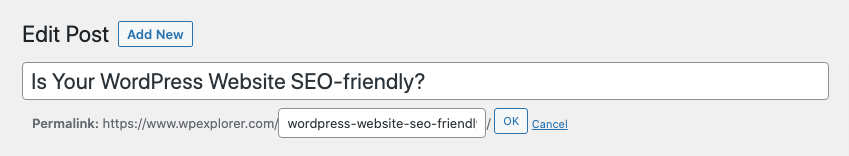
With your structure in place, you can also customize the slug for post and page links links while adding new content. When editing a new post or page, just click on the “Edit” button next to the permalink at the top of the editor.
There are some tips to help you understand how to better optimize URLs:
- categorize content
- avoid capital letters
- remove stop words (examples: a, an, as, it, may, of, to)
- use hyphens to separate words, not underscore
- add responsive URLs to the pages to indicate that you are mobile-friendly
- implement 301 redirects for pages with new URL destinations
There are also some plugins that will hint you at the most SEO friendly URLs but just using the SEO friendly tips above should be a great help.
4. Missing XML Sitemap
And important part of any website is the XML sitemap. This is a list of sorts that outlines your overall website structure so search engines can crawl your site and start indexing your pages. A sitemap is essential for every website, and it’s important that you don’t forget to create yours.
Ideally a sitemap will organize your site’s content in a natural way. Think of it as a tree with branches. For example, you have your blog, then blog posts, then for those posts you might have a category, author, title, etc.
You can manually create sitemaps, but luckily to create a WordPress sitemap you merely need to install a plugin. Most good SEO plugins will include XML sitemaps as a basic feature.
5. Improper Title Tags
The results in the search engines are displayed in such an order as a link, title tag, meta description. Since links are usually written in a small font and it is not the user’s first priority to look at the URL, they will discover the title at the beginning.
Search engines definitely pay attention to titles and may even rank well-visited sites lower, just because their title tag does not reflect the content of the article. It is easier to find pages with descriptive titles in the array of opened tabs and share them adequately on social media.
Therefore, aim to keep your titles 60 characters long (less if you use characters that take up more space as w, m, o), avoid all caps titles, don’t abuse keywords, and add your brand or site name at the end. The main advice though is to make it reflect the page’s content: witty and funny titles are creative but may not be the best option for SEO ranking.
6. Meta Description
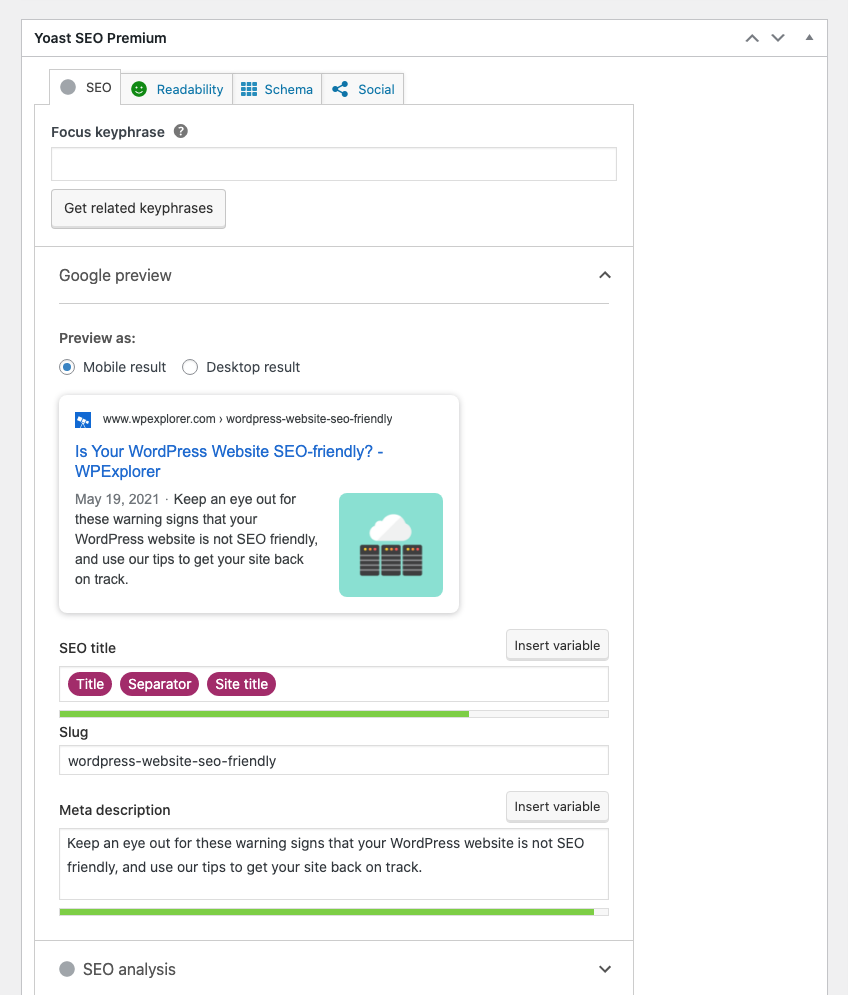
Meta descriptions aim at users rather than at search engines. It is a preview of the content, based on which users decide whether the web page is relevant for them. Consequently, a good meta description may become your pass into the world of high click-through rates.
Since Google tends to rank pages higher that are visited more often, using meta descriptions is an indirect way to step up your SEO game.
So what meta description should be like?
It has to be around 160 characters, contains easy words and short sentences, and actually explains what your page is about. It also makes sense to spice it up with some keywords (avoiding stuffing at all costs) and add a call-to-action. One of the best pieces of advice we have encountered is to treat your meta description as an ad: appeal to pain points and describe urgency. And again – using a plugin can make optimizing your meta description much easier (as seen the screenshot above).
7. Too Many Keywords
Search engines are not as close to the human as to actually read and evaluate the content. So they search for relevance, and the number of keywords correlates with it.
When SEO has first become a thing and algorithms were plain and straightforward, websites jammed many keywords in an article and it worked. What about today? Today there is such a thing as too much of a good thing, and keyword stuffing should be avoided.
Google does not only push for more relevant content but for better information as well. The reason why keyword stuffing drastically worsens the quality is that the text becomes very unnatural. Marketers come up with irrelevant sentences in order to use a specific keyword and you can see the same word repeating thrice in a three-sentence paragraph. That is why Google may rank pages lower where there are too many keywords.
When is it too much, you may ask? Well, search engines do not reveal their secrets but marketers at 3-5% keyword density.
Other tips for better keyword usage are diversity and variations. Google, for example, appreciates pages with a variety of keywords and synonyms much more than posts with the same word on repeat.
8. Duplicate Content
Content is not easy to produce, we get it. You always have to watch trends and put effort into writing or creating something. Yet, it is better to produce less content but to deliver a unique piece.
It is not just the question of morals. Search engines will simply rank the copied content the lowest, being ethical robots as they are.
Sometimes there is duplicate content on one website. For example, your product descriptions are very similar or have the same URL parameters. Therefore, try to differentiate descriptions on the website (and check whether they are not identical with other sites).
If it is about external duplicate content, avoid stealing or automatically rewriting content. Sometimes, you may plagiarize content without meaning to: after all, all kinds of sentences have been used on the Internet. Therefore, use a plagiarism checker to avoid any unintentional copying.
What if Someone Copies Your Content?
And if someone else has copied your content don’t be afraid to send them a message. You can request they add a rel=”canonical” tag linking to your site, which essentially gives your site credit as the original source (this is how Medium works when you choose to republish an article on their site). Or you can send a DMCA takedown notice if you want the offending site to simply remove the content they stole from you. Both are solid courses of action to deal with duplicate content on the web.
Bottom Line – SEO Is an Ongoing Process

SEO is not as easy today, as it was years ago. Yet, it is very doable to remove all the signs, described in the article. And you can manage most of them with the help of good hosting (like WP Engine) and an SEO plugin, both of which will significantly reduce the effort you spend on-page optimization.
Specifically, we like Yoast SEO which can help you pinpoint and resolve many of the warning signs above. Yoast Premium includes easy to use options to customize the SEO title, slug and meta. Additionally, the plugin offers automatic XML creating, a content “readability” check that will let you know if you have repeated content, and an SEO analysis that can tell you if you’ve used your keywords enough (or too much).
You can also invest in a premium service like ahrefs or Moz to help track, manage and improve your overall SEO. Both have plans that start at $99 per month and include SEO audit tools to that you can use to keep track of SEO warning signs.
If it is too overwhelming to implement all at once, take one step at a time. It is still better than doing nothing and letting search engines lower your rank due to such stupid reasons as a messy URL.




Thanks for the efficient tips Andrew!
I would also like to recommend Octopus.do for generating XML sitemap.
Hopefully you will find it helpful too😉