Beginner’s Guide to SEO: Intro, Prep & Jargon

- 1. Currently Reading: Beginner’s Guide to SEO: Intro, Prep & Jargon
- 2. WordPress Keyword Research and Usage for SEO
- 3. Improve SEO with Backlinks, Site Speed and More
In this concise guide, you will learn how to optimize your WordPress site, and cash in on the visitors you’ve been leaving on the table. In this part, you will be introduced to SEO, and shown some steps to take in preparation for the work to come. If you have problems understanding any terms or Jargon, refer to the “Deciphering the Jargon” section.
What Is SEO And Why Should You Spend Time On It?
If you don’t know, SEO stands for search engine optimization, and it is basically the discipline of getting search engines, often with a heavy focus on Google, to send you visitors.
SEO is complicated, and it can be hard to explain all that it entails without dragging on, so we’ll keep it short and sweet. The simplest way to explain SEO is to say that it is about communication. On one hand, knowing your potential audience and communicating to them in their language, on the other hand communicating to the search engines that your awesome content is worthy their bots’ attention and reverence.
SEO is often made out to sound like some kind of mystical, magical, endeavor. A voyage through murky seas that only the ‘gurus’ and experts can navigate (or gaming the results by ‘cheating the system’). And when it comes to breaking into the top 10 results on Google for the most competitive terms out there and maintaining your rank, maybe this is true.
But that’s not what this WordPress SEO guide is about. This guide will show you some best practices that can start getting you some small, but significant, search traffic that will add up over time.
When it comes to whether or not you should spend time on SEO as beginner, the blogging community seems to be split in half. People who blog about SEO “can not understate the importance of doing SEO”, whilst people who do Social Media, Networking, you name it, all kind of disregard it.
While I’ve seen some compelling stats that show that guest blogging traffic converts a better than search traffic, the potential volume is also quite different. While guest posts might bring in a few hundred visitors, thousands even, the potential lifetime traffic of getting a single post ranking is of a different scope. Even for some ‘measly’ search term that only gets 30 daily searches, that’s thousands of potential visitors per year (and of course, thankfully there’s no networking/cold emailing required). So let’s dig into WordPress SEO!
I Thought WordPress Was Already SEO Optimized?

Well, yes… and no. Correct structure is an important part of SEO, and WordPress has many key structures in place that makes it’s content more attractive for search engines. With extra plugins, for example WordPress SEO by Yoast, you can check a lot of boxes with almost no effort at all. But there are some things that have to be done, at least for now, more or less manually. Like optimizing your images, and making sure that your website is loading as quickly as it can. Or using header tags correctly when you are writing content. And making sure that your content is genuinely helpful and garners a share or three and a backlink or two.
But none of this matters if none is searching for what you’re writing about in the same way you’re writing about it.
While Google has made some progress when it comes to recognizing content that is helpful to the user even when the search terms don’t exactly match up with your use of keywords, there is still no real substitute for keyword research. As no matter how optimized your page is, if no one is searching for what you’re writing about, there’s nobody who will find it even if you rank at the top. (So don’t be too proud of ranking #1 for the exact match keyword for the name of your website. Although it can be useful for helping previous visitors get back to your site, it is very unlikely to get you any new eyeballs.)
Keyword Research
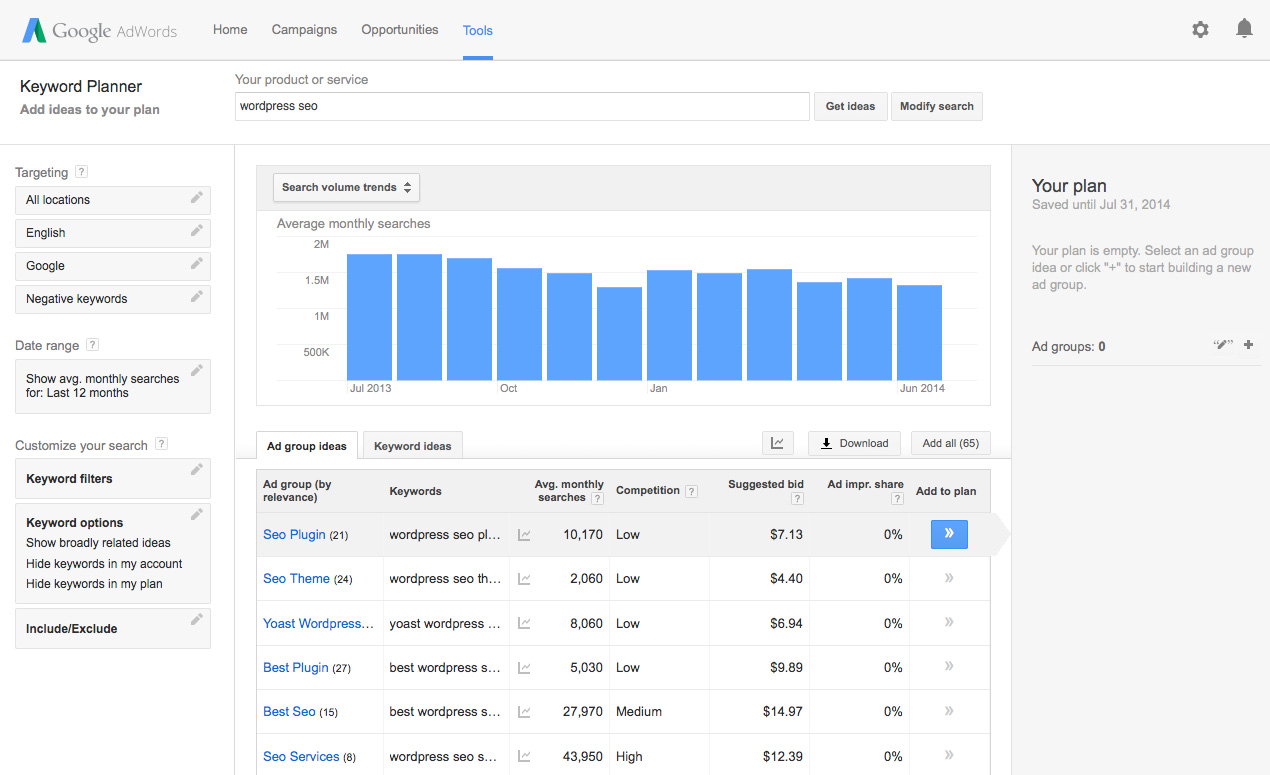
If you think about how a search engine works, by crawling and indexing your pages and your content, and then matching it up with requests made by the searchers, you can get a feel for what it’s all about. Search engine optimization, in a sense, is about communicating effectively to a potential audience. you have to know how to communicate with the audience.
And that’s where keyword research comes in. Keyword research is all about speaking the language of the potential visitor. A slightly different phrasing can mean a 1000% difference in potential audience. Sometimes more (but that doesn’t mean you should always target the more popular one, more on that later).
While there is a large number of software for doing keyword research out there, for the purposes of this guide, we are going to use the free alternative of Google Keyword Planner (you are going to need an active AdWords account to use it, which is easy enough if you already have a Google account – it’s free).
One of my favorite functions about the keyword planner is that you can use it to get suggestions and insights into the language your audience uses when searching for content, by simply typing in one broader topic, or problem.
The second part of keyword research, is assessing the competition. This is key, as it will help you decide whether or not it is worth your time to try to go after a specific keyword, or you should simply save it for later and move on to greener pastures.
SEO Best Practices According To Google
Google advises against “artificial link building”, including guest blogging to build backlinks. Instead Google advises you to:
- Optimize your website structure
- Write accurate page titles
- Improve your website urls
- Properly use meta descriptions
- Write kick ass content, or deliver kick ass services
- Properly use heading tags
- Optimize your images
Preparation
And now onto the actual doing. The following stuff will help you get your website ready for implementing the SEO best practices we will tackle in the next part of the guide.
Step #1 Make sure you allow search engines to index you.

LEAVE THIS BOX UNCHECKED! No matter how well you do all the other things, if you mess up on this step, it won’t matter at all. Your site will tell the googlebots, and the bingbots, and the yahoobots, that they’re “not welcome around here”. And they will move on, making you effectively invisible on most (if not all) search engines.
Step #2 Install an SEO plugin that picks up where WordPress leaves off.
One of the most used and recommended plugins, and the one we use here are WP Explorer, is WordPress SEO by Yoast (you will learn how to use it later, in detail, so there’s nothing to worry about).
Step #3 Get Your Site Indexed If It Isn’t Already
To get indexed by Google, you will need an already indexed website to link to your website, or you will need to manually get your website indexed. You can do this by submitting your sitemap (created easily by using a plugin like WordPress SEO by Yoast, or XML Sitemaps) using Google Webmaster Tools (to get indexed in Bing use Bing Webmaster Tools to submit your sitemap). More on creating an XML sitemap and submitting it here.
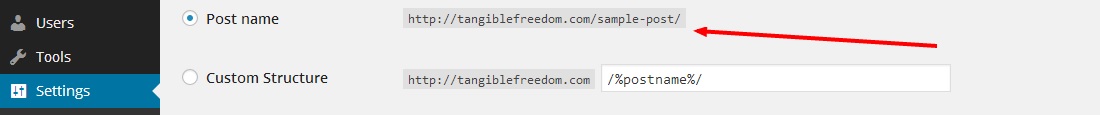
Step #4 Leave The Ugly Permalinks Behind
Not only is the default structure (p=999) bad for looks, it also indirectly damages your ranking, because having keywords in your page url does help a little bit. It’s such an easy fix too. Simply go to settings>permalinks and choose the “post name” link structure, and you’re all set.
Deciphering The Jargon
This is where we try to decipher some of the Jargon that’s often used when talking about SEO. If you have a term you’re wondering what means, feel free to leave a comment!
- Search volume = The amount of searches a specific keyword gets per month.
- Keyword = Most often refers to a word or phrase searched for in the, in the context of putting it into your content.
- Search phrase = Something someone searches for in search engines.
- Exact match keyword = Keyword that is the exact match to a search phrase (‘Organic Cat Food’ is an exact match but ‘Natural Cat Food’ is not).
- Backlink = A link from an outside website to a website or page.
- Permalink = The full url of a post (or page). Basically where you find a post when it’s no longer on the front page.
In this concise guide, you will learn how to optimize your WordPress site and get extra visitors you might be leaving on the table.
You’re off to a good start, and well on your way to better understanding and implementing good WordPress SEO practices. Hopefully you now have an idea of where to start with the SEO for your site. In my next post we’ll pick up with keywords, their importance and how to choose the best ones for your WordPress site – so stay tuned! And if you have anything to add, just leave a comment below. We’d love to hear what you have to say about SEO prep.



Great Post. very insightful. Getting site indexed is a tricky thing for beginners but you’ve explained it well.
very informative post. I will use the suggestions discussing here for optimizing my new blog site.This post will be very helpful for the begaineer SEO worker who are new in this field.
Keep posting this type of helpful post.
With best wishes.
Hi Ragnar Terjeson Miljeteig,
Thanks for such a great post about SEO.
Very clear concept and easy to understand.
Hope it will help many people.
absolutely amazing article! I must say that your post is really very good place to start and fun to read (especially the jargon). thanks for sharing it with us.
Hey, thank you for this article on seo basics. I have a better understanding now of terms. Thanks you!
This guide is incredibly helpful for SEO beginners. I appreciate the clear explanations and practical tips!